Fair Trade Economics Definition
In the commodities market fair trade price is the minimum price that importers must pay to the producers of some agricultural products such as coffee and banana. Fair Trade involves relationships that are.

Import And Export Social Studies Education Social Studies 3rd Grade Social Studies
Fair Trade is a labeling initiative aimed at improving the lives of the poor in developing countries by offering better terms to producers and helping them to organize.

Fair trade economics definition. By offering farmers the chance to reach out to customers in every corner of the globe individuals and families can fight poverty and build a brighter future. It enables them to improve their position and have more control over their lives Key aims of Fair Trade. Develop Transparent Accountable Relationships.
As a leader in the global movement to make trade fair Fairtrade supports and challenges businesses and governments and connects farmers and workers with the people who buy their products. Dragusanu Daniele Giovannucci Nathan Nunn. Fair Trade Investing.
Fair Trade is an approach to business and to development based on dialogue transparency and respect that seeks to create greater equity in the international trading system. This is embodied in several ways across the Fair Trade movement and the World Fair Trade Organization label is about the enterprises who produce what we buy verifying that they and their supply chain is fully committed to Fair Trade. Members of the fair trade movement add the payment of higher prices to exporters as well as improved social and environmental standards.
Basic fair trade philosophies call for. The fair trade model enables growers producers and companies based all over the world to showcase their products and fulfill their potential. Fair Trade is a strategy for poverty alleviation sustainable development.
Those objectives are often achieved by establishing direct trading relationships between small-scale producers in Africa Asia and Latin America and fair trade organizations FTOs in the. Fair Trade attempts to achieve several goals. Fair trade is a movement that believes it is unethical to pay producers in developing countries the market price if that price is too low to provide a sufficient quality of living.
1 Definition of Fair Trade Fair Trade is a trading partnership based on dialogue transparency and respect that seeks greater equity in international trade. Fair trade supports farmers and craftspeople in developing countries. Fair Trade is a set of business practices voluntarily adopted by the producers and buyers of agricultural commodities and hand-made crafts that are designed to advance many economic social and environmental goals including.
Fair trade global movement to improve the lives of farmers and workers in developing countries by ensuring that they have access to export markets and are paid a fair price for their products. In the context of the Fair Trade Movement a fair price is a price that when paid to the individual producers of a product such as coffee or handicrafts gives them access to a viable standard of living including nutrition health care education and cultural autonomy. The primary and best-known is to provide prices that deliver a basic livelihood for producers.
One of the driving forces behind the founders of Fair Trade was a desire to correct for multiple market failures in industries for many primary sector commodities. Fair trade is an arrangement designed to help producers in growing countries achieve sustainable and equitable trade relationships. As this project is concerned with defining those who will benefit the most from these fair trade.
Raising and stabilizing the incomes of small-scale farmers farm workers and artisans. A movement whose goal is to help producers in developing countries to get a fair price for their. Fair Trade certification a labeling initiative that offers better terms to producers and helps them to organize aims to offer ethically minded consumers the opportunity to help lift producers in developing countries out of poverty.
Ten Fair Trade Principles the first of which states that opportunities must be created for Economically Disadvantaged Producers. In a series of recent papers I have examined the causes and consequences of Fair Trade certification. Definition of fair trade Entry 2 of 2 1.
It is the floor price that must be paid irrespective of the market price. By requiring companies to pay sustainable prices which must never fall lower than the market price Fairtrade addresses the injustices of conventional trade which traditionally discriminates against the poorest weakest producers. Issue Date July 2014.
Fairtrades approach enables farmers and workers to have more control over their lives and decide how to invest in their future. In addition Fair Trade. Investing in companies or projects that promote fair trade with producers in developing nations.
These failures included the effects of monopsony power among transnational food processors and. The Economics of Fair Trade. The Fair Trade movement now covers over 650 producer organisations in more than 60 countries.
Trade in conformity with a fair-trade agreement 2.

What Is Fair Trade Definition And Examples Market Business News
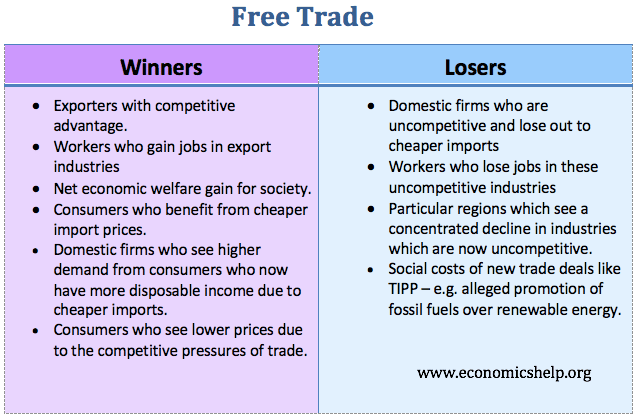
Who Are The Winners And Losers From Free Trade Economics Help

Its The Fourth Year Already Karen Templer Is Hosting Slow Fashion October We Fast Fashion Fashion Revolution Quotes Slow Fashion

Sustainability Frameworks Sustainability Environmental Justice Framework

Foreign Trade In Latin America And The Caribbean Infographic Economic Commission For Latin America And Economy Infographic Infographic Business Infographic
Free Trade Vs Fair Trade What S The Difference Sustainibabe

Advantages Of Globalization Http Theturbulencetraining Com Advantages Of Globalization Html Cross Cultural Communication Global Global Economy
Difference Between Free Trade And Fair Trade Difference Between

Tobin S Q Ratio Accounting And Finance Financial Strategies Financial Management

Difference Between Free Trade And Fair Trade With Comparison Chart Key Differences

Microeconomics And Macroeconomic Have Different Type Of Circular Flow This Circular Flow Is For Macroeconomic Study Info Macroeconomics Economics

Pin On G8 Free Trade Vs Fair Trade Unit
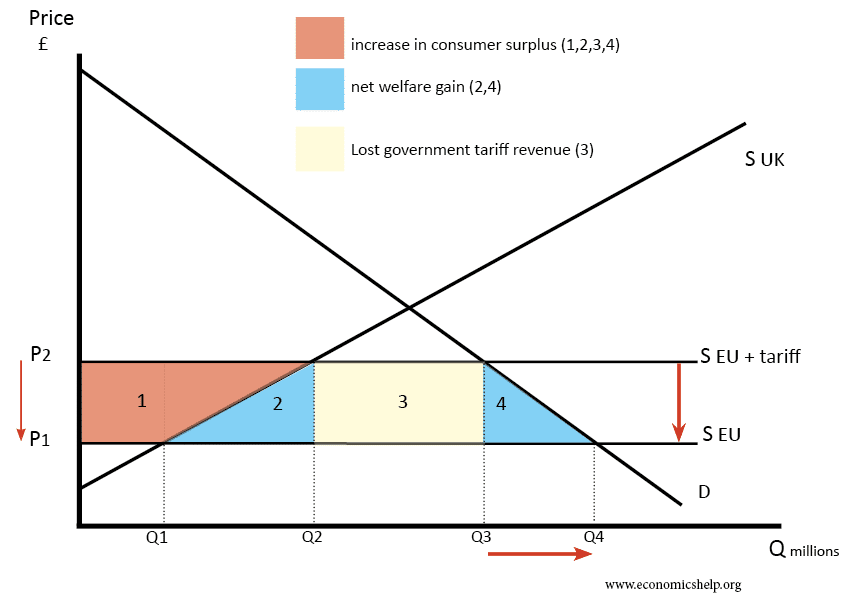
Benefits Of Free Trade Economics Help

Three Spheres Of Sustainability Sustainability Is About More Than Just The Environment Sustainability Environmental Justice Environment
Difference Between Free Trade And Fair Trade Difference Between

Sustainable Development Sustainability Sustainable Development Goals

What Is Fair Trade Definition And Examples Market Business News

Pin On Business And Marketing Illustrated
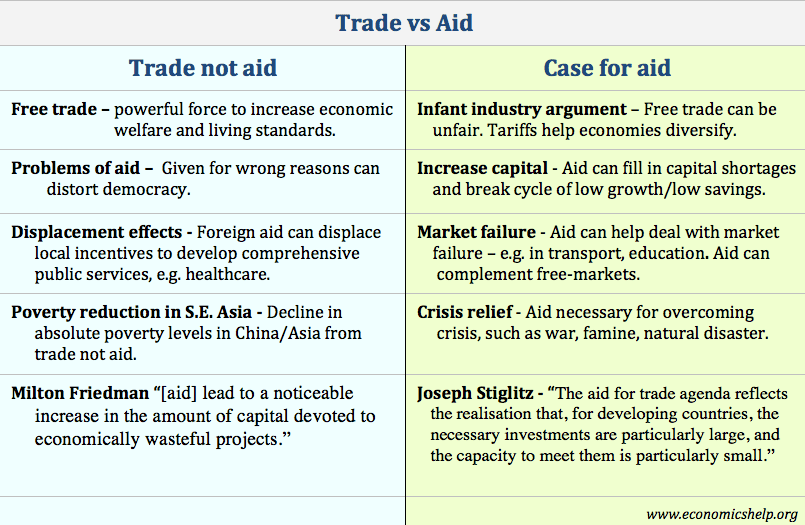

Post a Comment for "Fair Trade Economics Definition"